What is FDM 3d pritning?
What is FDM 3d printing?
Interested in learning the basics of FDM 3D printing? In this article, we explain why this technology is an efficient and cost-effective option for rapid prototyping and other applications.
Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) 3D printing, also known as Fused Filament Fabrication (FFF), is an additive manufacturing process in the field of material extrusion. FDM builds parts layer by layer by selectively depositing molten material along a predetermined path. It uses long filaments of thermoplastic polymer to form the final physical object.
FDM forms the largest installed base of 3D printers in the world, is the most widely used technology in most industries, and is probably the first process that comes to mind when you think of 3D printing.
In this article, we will introduce the basic principles and key characteristics of this popular additive technology. We also explore the differences between FDM machines built for prototyping (desktop) and industrial applications, and provide engineers with tips and tricks for getting the best results from FDM 3D printing.
How does FDM 3D printing work?
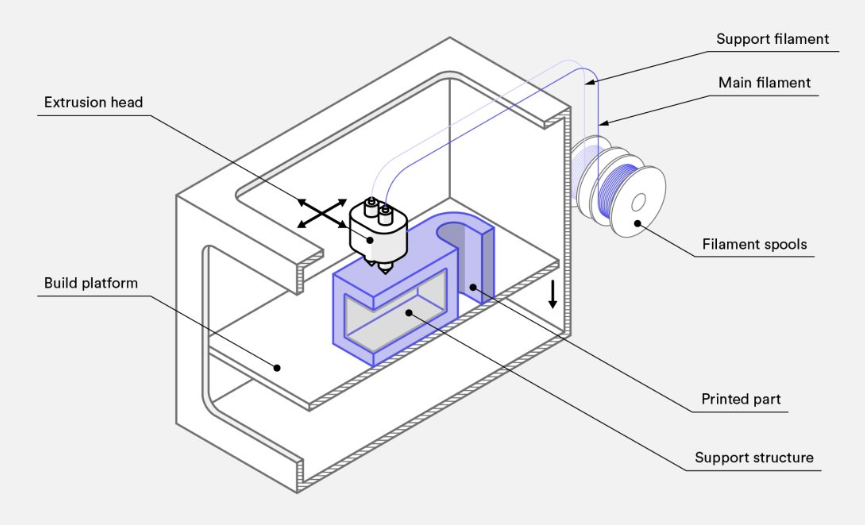
FDM 3D printers work by depositing molten filament material onto a build platform layer by layer until a complete part is obtained. FDM uses digital design files uploaded to the machine itself and converts them into physical dimensions. Materials for FDM include polymers such as ABS, PLA, PETG and PEI, which the machine feeds as threads through a heated nozzle.
To operate an FDM machine, you first load a spool of this thermoplastic filament into the printer. Once the nozzle reaches the desired temperature, the printer feeds the filament through the extrusion head and nozzle.
The extrusion head is connected to a three-axis system that allows it to move in the X, Y, and Z axes. The printer extrudes the molten material into filaments and deposits them layer by layer along a path determined by the design. Once deposited, the material cools and solidifies. In some cases, you can attach a fan to the extruder head to speed up cooling.
To fill an area, multiple passes are required, similar to coloring in a shape with markers. When the printer completes a layer, the build platform lowers and the machine begins printing the next layer. In some machine settings, the extrusion head moves upward. Repeat this process until the part is complete.
What are the printing parameters of FDM 3D printer?
Most FDM systems allow you to adjust multiple process parameters. These include nozzle and build platform temperatures, build speed, layer height, and cooling fan speed. If you're a designer, you usually don't have to worry about these adjustments because your AM operator probably already has them covered.
However, important factors to consider are build size and floor height. Common build dimensions for desktop 3D printers are 200 x 200 x 200 mm, while industrial machines can be as large as 1,000 x 1,000 x 1,000 mm. If you prefer to use a desktop computer to print parts, you can break down the large model into smaller parts and then reassemble them.
Typical layer heights for FDM are 50 to 400 microns. Printing shorter layers produces smoother parts and captures curved geometries more accurately, but printing taller layers allows you to create parts faster and with a lower price tag.

 EN
EN
 AR
AR
 BG
BG
 HR
HR
 DA
DA
 NL
NL
 FR
FR
 DE
DE
 EL
EL
 HI
HI
 IT
IT
 JA
JA
 KO
KO
 PT
PT
 RU
RU
 ES
ES
 SV
SV
 TL
TL
 ID
ID
 SR
SR
 SK
SK
 UK
UK
 VI
VI
 ET
ET
 HU
HU
 TH
TH
 TR
TR
 MS
MS
 GA
GA
 BE
BE
 HY
HY
 KA
KA
 LO
LO
 LA
LA
 MN
MN
 NE
NE
 SO
SO
 MY
MY
 KK
KK
 UZ
UZ
